General Formulas
Petrol Emissions Formula
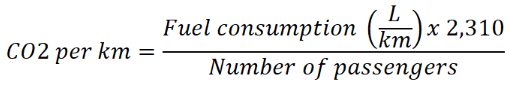
Grid Emission Factor
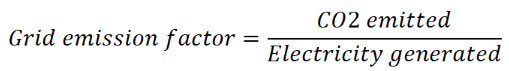
Diesel Emissions Formula
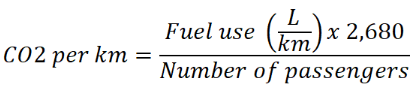
Electric Emissions Formula
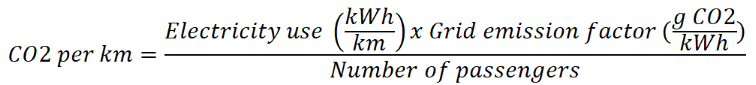
1. Car
A car can pollute through various mechanisms depending on its propulsion method, whether it's petrol, diesel, or electric power. Electric cars have direct CO₂ emissions of zero, as they do not emit exhaust when driving. The average CO₂ values for petrol and diesel vehicles refer to newly registered cars in Europe, based on the latest EEA benchmarks. Petrol Car: 122 gCO₂/km Diesel Car: 148 gCO₂/km Electric Car: 0 gCO₂/km2. Bus
Bus transport is a key mobility mode in cities and regions, with environmental impacts that vary by vehicle type, fuel, and occupancy. Because buses allow shared travel, emissions per passenger can be much lower when they are well-filled. We do not differentiate between urban, regional, or intercity buses, as emissions are calculated using mileage and average efficiency. Although electric and hydrogen buses can greatly reduce CO₂ emissions, our app does not include electric buses due to insufficient reliable data. Diesel Bus : 80g of CO₂/km/passenger3. Airplane
Air travel is one of the most polluting forms of transport in Europe, if not the most polluting. Emissions can vary depending on the type of flight and the technology used, but generally remain high due to high fuel consumption. Long-journey flights and older aircraft are particularly polluting. Unlike energy innovations in other modes of transport, such as cars, the possibility of creating an electric aircraft is much more complicated due to battery life and boarding capacity. We decided not to differentiate between long-journey, small, and medium-journey flights because we plan to calculate CO₂ emissions based on mileage. For example, some domestic flights are longer than some international flights. Therefore, we calculated an average. Plane : 225g CO₂/km/passenger.4. Train
Emissions for electric trains can vary by country depending on the electricity mix, and are generally lower in countries with a high share of renewables or nuclear power. Diesel trains remain significantly more polluting per passenger-kilometer, although improvements in efficiency have helped reduce average emissions in Europe. Diesel Train: 63 gCO₂/km Electric Train: 5 gCO₂/km5. Scooter
Electric scooters, which have been popular for several years, are growing rapidly in major European cities. Their emissions are generally low due to being used mostly for short journeys, especially in countries where electricity is based on renewable energy or nuclear power. As a result, CO₂ emissions from electric scooters depend mainly on manufacturing, which accounts for 79% of emissions, and logistics, which includes collection and recharging. Scooter : (60/0.79) → 34g CO₂/km/passenger.6. Ferry
Despite the much lower use of ferries compared to Norway or other Nordic countries, ferries are among the most polluting forms of transport. According to the EEA, ferries can emit 267g of CO₂ equivalent per kilometer. Furthermore, the EEA does not provide any figures for cruise ships, but we can assume that their carbon footprint is similar to that of ferries. Diesel ferry : 267g CO₂/km/passenger.7.Walking/Bicycle
People travelling on foot do not produce any direct CO₂ emissions, as we do not take into account CO₂ emissions produced by food or personal equipment. In addition, for direct CO₂ emissions from people travelling by bicycle, these are very low or even zero, as we do not take into account the energy used in manufacturing the bicycle or the energy provided by the food consumed by the cyclist. However, electric bicycles require electricity to operate. Walking : 0 g CO₂/km Traditional bike : 0g CO₂/km Electric bike : 3g CO₂/km8. Motorcycle
Motorcycle emissions vary depending on the type of engine and fuel used. Diesel motorcycles remain more polluting per kilometer traveled, while gasoline motorcycles, although slightly less polluting, also contribute significantly to CO₂ emissions and local pollutants. However, technical improvements and European standards have gradually reduced average emissions (Clairotte et al., 2020). As the difference is not significant, we have decided to take an average of the two types of fuel : Motorcycle diesel/petrol : (89 and 112) → 100 g CO₂/km/passenger.